Why Enterprise SEO Is a Core Growth Lever for Large Companies
For large companies, SEO is a durable, compounding growth engine that lowers acquisition costs, strengthens brand authority, and drives measurable revenue impact across markets and business units. Unlike small-site SEO, enterprise SEO operates across thousands to millions of URLs, diverse customer journeys, complex tech stacks, strict compliance requirements, and multiple countries and languages. The strategies that win at this scale are systematic, data-informed, and embedded into product, marketing, and engineering workflows.
Enterprise leaders should treat SEO as a product: with a roadmap, governance, SLAs, experimentation, and an operating model that aligns stakeholders. The companies that outperform do five things consistently:
- Translate business goals into search opportunities and defensible positions in the SERP.
- Engineer a crawlable, performant site architecture that scales.
- Build a high-velocity content engine with quality controls and brand governance.
- Automate routine work (monitoring, QA, internal links, schema) without sacrificing judgment.
- Measure impact with executive-level reporting tied to revenue and efficiency.
This approach mitigates common pitfalls such as index bloat from faceted navigation, thin and duplicate content from legacy templates, inconsistent international canonicals, and delays caused by unclear ownership across teams. When SEO is embedded as a cross-functional practice instead of a marketing silo, it improves discoverability, supports product discovery, reduces paid search dependency, and informs strategy across channels.
Use the blueprint below to refresh or rebuild your enterprise SEO program. It’s designed to work whether you are consolidating brands, replatforming, expanding internationally, or scaling content production.
Key priorities to align before you start:
- Define your growth levers: categories, product lines, solutions, use cases, and stages of the buyer journey where organic can lead or assist.
- Establish guardrails: brand, legal, compliance, and accessibility requirements that shape what you can publish and how.
- Choose your architecture path: how taxonomy, internal links, and templates will scale cleanly across markets and languages.
- Agree on measurement: shared definitions for visibility, quality traffic, pipeline, revenue contribution, and cost efficiency.
- Resource for speed: ensure product, engineering, and content have capacity for iterative delivery, not one-off projects.
I’m Chris Robino, a Digital Strategy Leader and AI & Search Expert with over two decades of experience helping large organizations systematize SEO for sustained growth. The guidance that follows focuses on strategies and operating models proven to work at enterprise scale.
A Blueprint for Enterprise SEO at Scale
Starting or upgrading an enterprise SEO program is less about hacks and more about systems. The goal is to ship a technically sound, content-rich, and continuously improving web experience that search engines can understand and users love.

1) Set Objectives and Guardrails
- Tie objectives to revenue and efficiency: incremental qualified sessions, assisted pipeline, conversion rate lift, and lower blended CAC.
- Define target themes and SERP real estate to win: category head terms, long-tail use cases, solution pages, help and education content, product and support.
- Establish approval workflows and legal/compliance guardrails to keep velocity high without risking brand or regulatory issues.
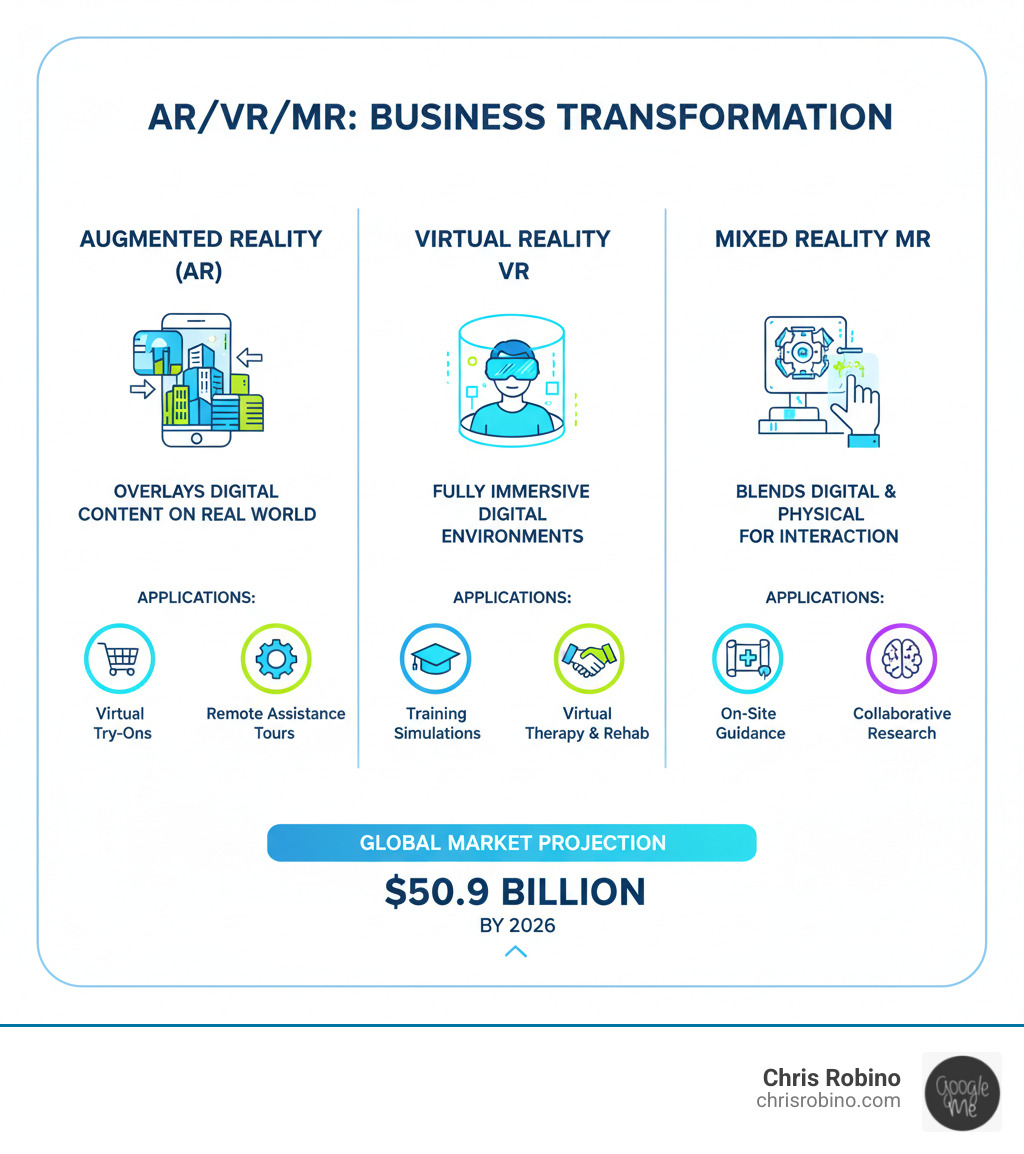
- Consider how emerging technologies impact search behavior – for instance, understanding the difference between AR and VR can inform content strategy for tech-focused enterprises.
2) Technical Foundations at Scale
- Crawl management and indexation: use robots.txt, meta robots, and parameter handling to prevent index bloat. Canonicalize near-duplicates. Clean up erroring or redirecting URLs in sitemaps. Split sitemaps by type and size for freshness and diagnostics.
- Information architecture: design a clear, hierarchical taxonomy with hub-and-spoke internal linking. Use breadcrumb markup. Avoid orphan content and deep, fragile navigation patterns.
- Pagination and facets: implement rel=”next”/”prev” patterns where appropriate, curate linkable views for high-value facets, and block low-value combinations.
- Internationalization: use correct hreflang and consistent canonical strategy. Decide on ccTLDs, subfolders, or subdomains based on governance, infrastructure, and equity considerations.
- Rendering and JS: prefer server-side rendering or hybrid rendering where needed. Defer non-critical scripts, reduce JS payloads, and ensure content is available to crawlers without fragile execution paths.
- Performance and Core Web Vitals: set performance budgets per template; optimize images (next-gen formats, responsive sizes), use efficient caching, preconnect/prefetch critical resources, and monitor real-user metrics.
- Structured data: implement Organization, Product, Article, FAQ, HowTo, Breadcrumb, Sitelinks searchbox, and local business schema where relevant. Maintain automated validation and alerting for schema regressions.
3) Content Engine and Governance
- Topic strategy: cluster around entities and problems customers actually search for. Map content to the full journey (awareness, consideration, decision, post-purchase/support).
- Templates that scale: create modular page templates for categories, product/solution pages, comparison pages, use cases, FAQs, and resources so you can publish consistently without reinventing the wheel.
- Programmatic pages with quality controls: generate at scale where data quality is high (location, inventory, product attributes, documentation), with strict deduplication and human editorial review.
- E-E-A-T and brand consistency: use clear authorship, expert review for sensitive topics, and transparent sourcing. Align tone and claims with brand and legal guidelines.
- Refresh and consolidation: schedule systematic updates for content decay. Merge thin or overlapping assets, redirect to winners, and preserve signals.
- Media diversification: support text with helpful images, diagrams, short videos, and downloadable assets. Optimize all media for speed and search findy.
- Learn from research on the business impact of extended reality to understand how immersive content formats may shape future SEO strategies.
4) Internal Linking Strategy
- Build hub pages that concentrate authority and clarify topical ownership.
- Automate internal link suggestions using rules and models while allowing manual curation for priority pages.
- Use breadcrumbs, related links, and contextual anchors to improve findy and relevance.
5) SERP Features and Findability
- Target rich results with accurate schema and content that genuinely answers user intent.
- Optimize for image, video, and news surfaces when they matter for your categories.
- Ensure brand elements (logo, social profiles, sitelinks, searchbox) are eligible and accurate.
6) International and Local at Scale
- Choose a scalable structure for global expansion. Localize beyond translation: pricing, measurements, cultural references, and compliance notices.
- Use in-market editorial review and native keyword research to avoid literal translations that miss searcher language.
- For physical locations, maintain accurate listings, consistent NAP data, localized landing pages with unique value, and appropriate local schema.
7) Measurement and Diagnostics
- Instrument clean analytics with consistent conversion definitions across properties.
- Track visibility, indexation health, template performance, Core Web Vitals, and structured data health. Use log-file insights to validate crawl behavior and prioritize fixes.
- Build an executive dashboard that ladders organic outcomes to pipeline, revenue, and efficiency.

8) Risk Management and Migrations
- For rebrands, consolidations, and platform changes, use a repeatable playbook: crawl and inventory, mapping, test environments, parity checks, redirect matrices, staged rollouts, and rollback plans.
- Establish change control for navigation, templates, and critical metadata to prevent accidental regressions.
The blueprint above balances technical rigor with content scale, enabling large organizations to move fast without sacrificing quality or compliance.
Scaling and Future-Proofing Your Enterprise SEO Program
As your program gains traction, the challenge shifts from launching initiatives to sustaining velocity, quality, and resilience. That requires an operating model, tooling, automation, and a culture of experimentation.

Operating Model and Governance
- Create a Center of Excellence that defines standards, templates, and QA, with embedded practitioners in product and regional teams.
- Clarify ownership using RACI across strategy, content, engineering, analytics, and legal. Set SLAs for tickets that impact crawlability, performance, and indexation.
- Implement a documented intake and prioritization process so high-ROI work rises to the top.
Tooling and Automation
- Use an enterprise crawler and site monitor to detect changes, errors, and regressions by template and locale.
- Analyze server logs to see actual crawl behavior, spot waste, and identify bottlenecks.
- Automate sitemap generation, schema deployment, internal link suggestions, and change detection. Pair automation with human review for relevance and brand safety.
- Maintain a release checklist for SEO-critical fields to prevent missing titles, canonicals, hreflang, or schema during deployments.
AI-Assisted Scale with Human Oversight
- Leverage AI for keyword clustering, brief creation, entity and outline suggestions, and structured data generation.
- Keep humans in the loop for fact-checking, policy compliance, brand tone, and originality. Measure outcomes so AI usage demonstrably improves quality and speed.
Experimentation and Learning
- Run SEO-safe experiments on templates or internal linking patterns. Avoid cloaking or serving materially different content to users vs. crawlers.
- Document hypotheses, treatments, and results. Roll wins into standards and deprecate underperforming patterns.
Forecasting, Budgeting, and Prioritization
- Create bottom-up forecasts by opportunity cluster and template. Use historical baselines, click-share estimates, and expected conversion to revenue to size the prize.
- Prioritize with a transparent framework (e.g., impact, confidence, effort) and communicate trade-offs to stakeholders.
- Tie budgets to proven levers: speed, crawl efficiency, content throughput, and conversion lift from UX/technical improvements.
Cross-Channel and Cross-Functional Synergy
- Share search insights with paid media to reduce cannibalization, capture demand, and inform creative. Coordinate messaging and landing experiences.
- Align with PR and comms so earned coverage and thought leadership support entity authority and link acquisition.
- Partner with product and CX to ensure on-site search, navigation, and documentation reflect how customers describe problems.
Compliance, Accessibility, and Risk
- Bake accessibility (WCAG) into templates and QA so you improve both user experience and indexability.
- Ensure privacy and data collection policies are reflected in tracking and consent mechanisms, especially across regions with different rules.
- Maintain legal review paths for sensitive claims and regulated content.
Migrations and Major Releases
- Treat every large change as a program: discovery, mapping, pre-launch audits, controlled rollouts, monitoring, and post-launch remediation.
- Track parity of critical elements: URLs, metadata, headings, schema, internal links, and performance. Validate redirects and indexation continuously.
Prepare for What’s Next in Search
- Expect more blended, entity-based, and answer-focused experiences. Structure your data, clarify topical authority, and ensure your content genuinely solves problems.
- Build content that’s helpful, current, and supported by expertise. Consolidate fragments into comprehensive resources where it improves usefulness.
- Invest in performance and clean architecture so you remain resilient as algorithms emphasize quality and user experience.
Your Next Steps
- Identify three high-ROI opportunity clusters and ship template-level improvements that benefit hundreds or thousands of pages at once.
- Launch a content refresh program focused on decayed winners and fragmented clusters.
- Stand up executive dashboards that report impact in business terms and establish a quarterly roadmap tied to revenue goals.
- Formalize governance, release checklists, and SLAs so SEO quality is preserved as you scale.
When enterprise SEO is run like a product—with clear ownership, disciplined execution, and relentless iteration—it becomes a compounding, defensible advantage that supports brand leadership and sustainable growth.
