Why Understanding Robotics Process Automation Matters Now
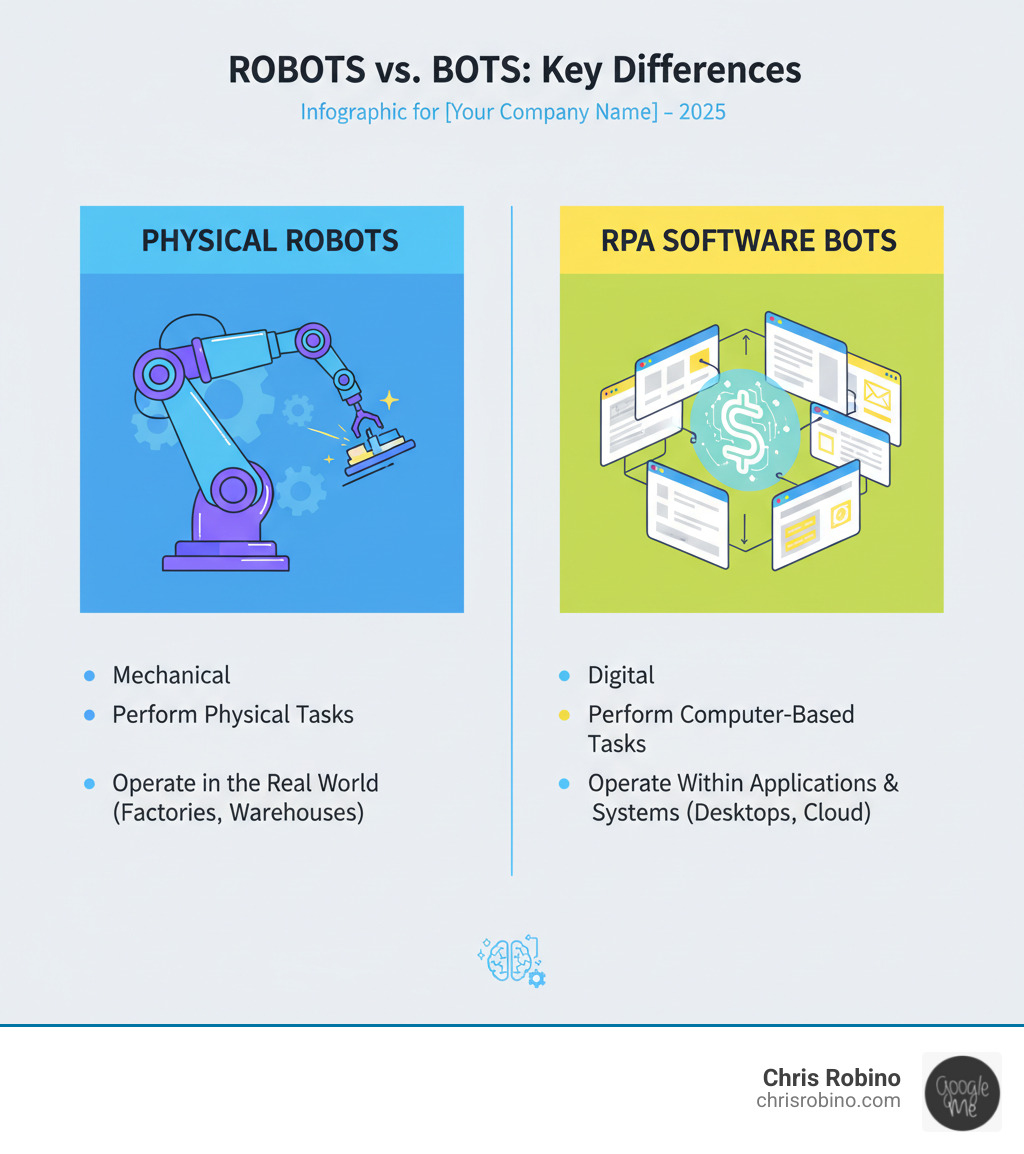
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a software technology that uses digital “bots” to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. These bots mimic human actions to perform tasks like data entry, form processing, and moving files between applications. Despite the name, RPA involves no physical machines; it’s software that interacts with computer systems through the user interface, just like a person would.
Think of it as a digital assistant that handles the tedious parts of your workday, working 24/7 without errors. This frees employees to focus on higher-value work, reducing costs and improving accuracy.
The technology is already a cornerstone of modern digital strategy. With internet search being the top channel for B2B product findy, understanding automation is critical. Research shows 86% of SEO professionals have adapted AI into their strategies, and RPA is a key part of this trend.
However, many business leaders find explanations of RPA either too technical or too vague. This guide cuts through the confusion to explain what RPA is, how it differs from AI, and where it fits into your business.
As Chris Robino, I’ve spent over two decades guiding organizations through digital change. I’ve seen how a strategic approach to Robotic Process Automation can transform a business—and how a lack of strategy can lead to failure.
The Ultimate Guide to Robotics Process Automation
Robotics Process Automation is about efficiency. It frees people from repetitive tasks to focus on work that requires human intellect and creativity, forming a key part of modern AI-Driven Business Solutions.
What is Robotics Process Automation and How Does It Work?
First, let’s be clear: RPA uses software “robots,” not physical ones. These are digital workers that mimic human actions on a computer, executing mundane, repetitive tasks by following a set of instructions.
Think of RPA as a low-code technology that observes a user’s actions across different applications and then replicates them. The bot interacts with systems via the graphical user interface (GUI), just like a person does. This allows it to automate processes even on legacy systems that lack modern APIs for integration.
To understand RPA’s unique role, it’s helpful to compare it with traditional automation and artificial intelligence (AI).
- Traditional Automation usually requires custom coding and deep system integrations via APIs. It’s powerful but often complex and inflexible.
- Robotics Process Automation operates at the presentation layer (the UI), making it faster to implement and more adaptable to existing systems without deep integration.
- Artificial Intelligence mimics human intelligence, not just actions. AI learns from data, makes predictions, and handles complex problems. While RPA follows a script, AI can write new ones.
RPA and AI are complementary. AI can give RPA bots the ability to handle more complex tasks, like understanding documents or interpreting images. As Professor Leslie Willcox notes in What knowledge workers stand to gain from automation, this technology can take the “robot” out of the human, freeing people for higher-value work.
| Feature | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Traditional Automation | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intelligence | Rule-based, mimics human actions | Programmed logic, executes predefined scripts | Data-driven, learns, predicts, understands, adapts |
| Data Handling | Structured data, operates on existing interfaces | Structured data, deep integration with databases/APIs | Structured and unstructured data, cognitive processing |
| Integration | User Interface (UI) interaction, surface-level integration | API-based, deep system integration | API-based, integrates with data sources and cognitive services |
| Complexity | Automates repetitive, high-volume tasks | Automates well-defined, stable processes | Solves complex, ambiguous problems, requires large datasets |
| Learning | Does not inherently learn or adapt without AI augmentation | Does not learn | Learns and improves over time |
| Primary Goal | Reproduce human-directed tasks | Execute programmatic functions | Mimic human intelligence, decision-making |
The Business Case: Core Benefits and Real-World Applications
RPA adoption is growing rapidly because it delivers clear business value. The core benefits include:
- Increased Efficiency and Speed: Bots work 24/7, completing tasks much faster than humans.
- Higher Accuracy: Automation eliminates human error, improving data quality and consistency.
- Cost Reduction: Automating high-volume tasks delivers significant ROI.
- Improved Employee Morale: Freeing staff from tedious work increases job satisfaction and allows them to focus on more strategic activities.
- Better Compliance: RPA provides a clear audit trail for every automated action, simplifying regulatory reporting.
- Scalability: Easily scale automation up or down to meet business demand without adding headcount.
These benefits translate into a better customer experience through faster, more accurate service.
RPA is applicable across any industry with rule-based digital tasks. Common use cases include:
- Finance and Accounting: Invoice processing, account reconciliations, and financial reporting.
- Healthcare: Patient data management, claims processing, and billing.
- Human Resources: Employee onboarding, payroll processing, and benefits administration.
- Customer Service: Automating responses, routing inquiries, and updating customer records.
- Government: Processing benefits, renewing licenses, and ensuring compliance with mandates like the OMB’s M-18-23, “Shifting From Low-Value to High-Value Work.”
Implementing RPA is a key part of the Technology Trends for Business that are defining modern competitive advantage.
Navigating Challenges and Key Implementation Factors

While RPA offers significant benefits, successful implementation requires a strategic approach to steer common pitfalls. Many programs struggle to scale beyond initial pilots due to challenges with process selection, cultural resistance, and maintenance.
To ensure success, consider these key factors:
- Strategic Process Selection: Don’t automate broken processes. Use process mining and analysis to identify high-impact, rule-based, repetitive tasks. Avoid processes that require complex human judgment.
- Manage Cultural Change: Address employee concerns head-on with clear communication. Frame RPA as a tool to augment human capabilities, not replace them. Invest in training and upskilling to prepare your team for new, higher-value roles.
- Establish Strong Governance: Create a Center of Excellence (CoE) to manage your RPA strategy, set standards, and ensure security and compliance. As noted in the MIT Sloan Management Review article, “Five Robotic Process Automation Risks to Avoid“, strong governance is crucial to prevent new risks.
- Plan for Maintenance: RPA bots interact with application UIs, so system updates can break them. Plan for ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure bots remain functional.
- Start Small, Think Big: Begin with a pilot project to demonstrate value and build momentum. Use these early wins to justify a broader, enterprise-wide automation strategy.
These principles are central to effective AI Implementation Strategies and are critical for driving successful digital change.
The Evolution and Future of Robotics Process Automation
RPA is no longer just simple task automation. Its evolution reflects a journey toward greater intelligence.
Initially, RPA focused on basic, rule-based task automation. Today, it has merged with AI technologies like machine learning and natural language processing to create Intelligent Automation (IA). These smarter bots can now process unstructured data, understand documents, and handle more complex cognitive tasks.
The next frontier is Hyperautomation. This approach uses a combination of RPA, AI, and process mining to not only automate tasks but also to find and analyze which processes are best suited for automation. In this model, AI acts as the “brain” that plans and adapts, while RPA acts as the “hands” that execute tasks across enterprise systems.
This synergy between RPA and AI is key. AI gives RPA the ability to handle exceptions and make decisions, making it possible to automate more of the complex, real-world processes that businesses rely on.
Impact on the Workforce
The rise of automation naturally raises questions about employment. The focus is on job evolution, not just job elimination. RPA automates routine tasks, allowing employees to be redeployed to more strategic, creative, and engaging work. This shift creates demand for new roles like automation specialists, process analysts, and RPA developers. The goal is to “take the robot out of the human,” enabling people to focus on what they do best.
The future of RPA lies in this deeper integration with AI, creating adaptive, self-learning automation solutions. This evolution is one of the core Future Business Technology Trends that will continue to reshape how we work.
Integrating Automation into Your Digital Strategy
Digital change isn’t about adopting technology for its own sake; it’s about using tools that deliver real business value. Robotics Process Automation is a foundational technology that does just that.
The goal of automation is to create space for your team to do their best work. By automating repetitive tasks like data entry and report generation, RPA gives you a way to reclaim your team’s time and redirect it toward innovation and strategic problem-solving. It’s not about replacing people—it’s about replacing the robotic parts of their jobs to open up human potential.
However, many organizations fail by treating RPA as a standalone IT project. To succeed, automation must be part of a cohesive digital strategy that supports your core business objectives, whether that’s improving customer experience, accelerating time-to-market, or strengthening compliance. Automation should build your competitive advantage, not just cut costs.
Successful implementation requires both technical knowledge and organizational insight. My work with organizations has shown that a strategic approach creates a virtuous cycle: early wins build confidence, freed-up capacity drives innovation, and improved accuracy strengthens customer trust.
As RPA continues to merge with AI, the opportunities will only grow. The core principle remains the same: technology should serve your people and your purpose. If you’re ready to explore how automation fits into your digital strategy, it’s crucial to have guidance that bridges technical capabilities with the human side of change.
Learn how a Technology Innovation Consulting Firm can help you steer this journey with clarity and confidence.
