Why Your Business Needs a Cloud Adoption Strategy
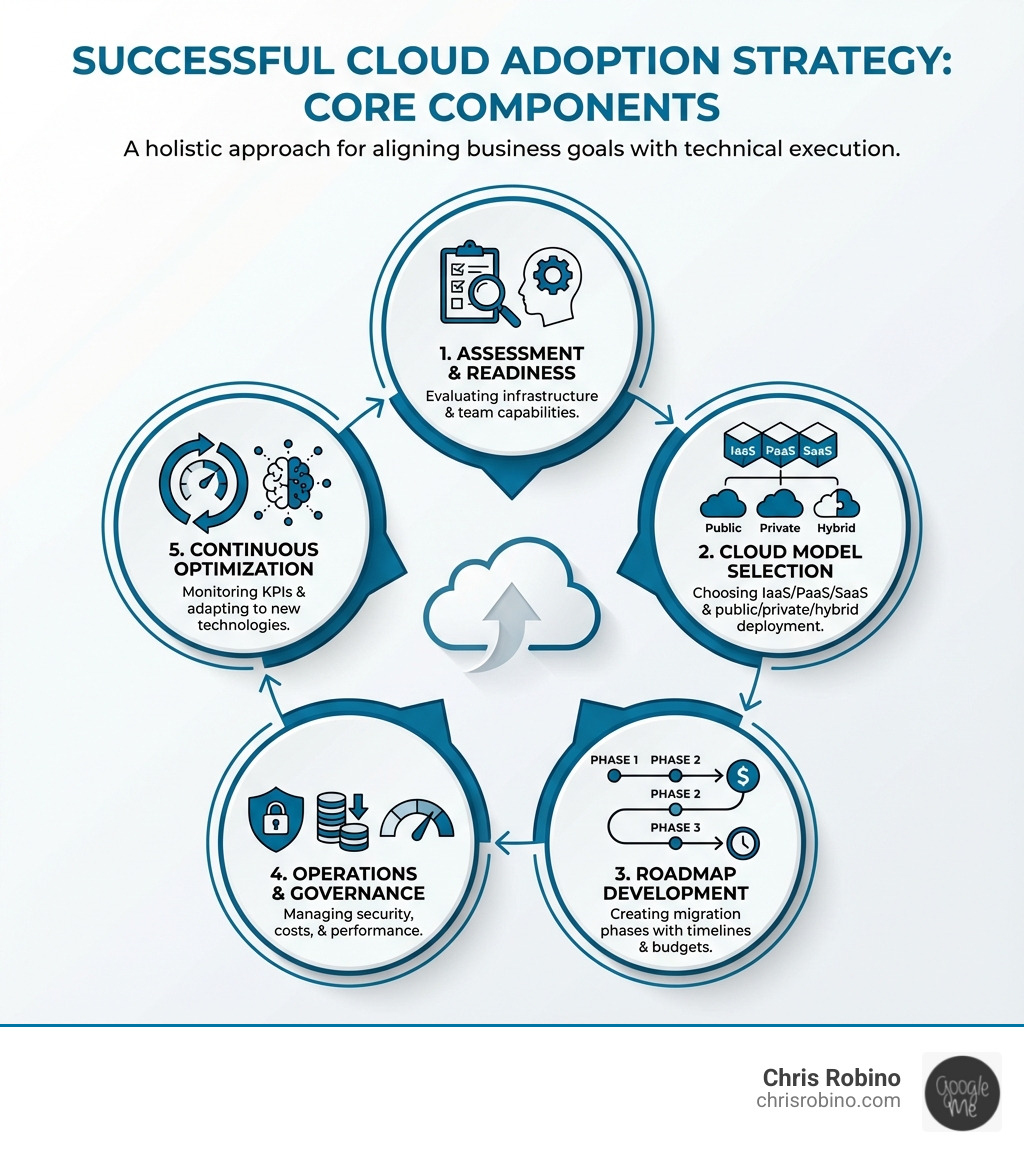
A cloud adoption strategy is a comprehensive plan for moving to the cloud. It covers why you’re migrating, what moves first, how to manage costs, and who is responsible. Key components include:
- Assessment: Evaluating current infrastructure and organizational readiness.
- Service & Deployment Models: Choosing between IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS and public, private, or hybrid environments.
- Roadmap: Creating a phased migration plan with timelines and budgets.
- Operations & Governance: Establishing security, cost management, and optimization practices.
- Skills & Culture: Addressing talent gaps and preparing teams for change.
Without a strategy, businesses risk cloud sprawl—wasted budgets, security gaps, and missed opportunities. Public cloud spending reached over $631.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit $1.8 trillion by 2029. The challenge isn’t if you should adopt the cloud, but how to do it right.
Successful adoption aligns business goals with technology, prepares people for change, and balances speed with security. Today, 89% of organizations use a multi-cloud approach, and 73% operate hybrid environments. However, the biggest hurdle remains a talent shortage, with a lack of qualified staff being the top barrier to cloud adoption.
I’m Chris Robino, a Digital Strategy Leader with over 20 years of experience helping organizations steer digital change. I connect business objectives with technology execution to ensure cloud strategies are practical, measurable, and drive growth. This guide provides actionable frameworks for your entire cloud journey, from assessment to optimization.
A well-defined cloud adoption strategy open ups scalability, agility, and competitiveness. It’s how you realize value from cloud investments, align teams, and mitigate modernization risks.
Step 1: Assessment and Readiness Evaluation
Before migrating, you need to assess your assets and team readiness. This initial phase is critical.
- Business Alignment: Your cloud adoption strategy must support key business goals, whether it’s cost reduction, faster innovation, or improved customer experience. Defining these drivers helps prioritize decisions. Business and Technology Consulting can help clarify these objectives.
- Technology Assessment: Evaluate your current IT infrastructure, applications, and data. Identify dependencies, data sensitivity, and compliance needs to determine what to move, what to keep on-premises, and what to modernize.
- People and Culture: Cloud adoption requires new skills, mindsets, and workflows. Secure leadership buy-in, foster a culture of learning, and ensure teams understand the benefits and new processes to bridge the gap between technology and business.
- Governance and Security: Establish clear policies for data protection, access control, and compliance from the start. Assess security risks to build a secure and compliant cloud environment.
Step 2: Choosing Your Cloud Models
Once you understand your goals, choose the right service and deployment models for your needs.
- Cloud Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS):
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources like servers and storage. You manage the OS and applications, offering maximum control.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a complete development and deployment environment. You focus on applications while the provider manages the infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers fully managed applications over the internet, such as email or CRM.
These models are often used in combination.
| Service Model | Description | Control Level | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| IaaS | Virtualized computing resources, storage, network | High | Hosting websites, data analysis, custom apps |
| PaaS | Development platform, runtime environment | Medium | Application development, API management |
| SaaS | Fully managed software application | Low | Email, CRM, collaboration tools |
- Cloud Deployment Models (Public, Private, Hybrid, Multi-Cloud):
- Public Cloud: Services from third-party providers over the public internet, offering high scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated cloud infrastructure for a single organization, providing improved security and control for sensitive data.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them for greater flexibility.
- Multi-Cloud: Uses services from multiple public cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize costs. Today, 89% of organizations report using a multi-cloud approach, with 73% of those being hybrid environments.
Choosing the right model depends on your security needs, budget, and workloads. For example, Cloud Solutions for Media often use hybrid models for content storage and distribution.
Step 3: Creating and Executing the Roadmap
With your models chosen, it’s time to chart your course with a clear roadmap.
- Developing a Migration Plan: Outline the steps, resources, and budget for your cloud journey. Prioritize applications based on business value and complexity, planning for minimal disruption.
- The 7 R’s of Migration: Use this framework to decide how to handle each application:
- Rehost (Lift and Shift): Move applications as-is. It’s fast but may not be optimized for the cloud.
- Replatform: Make minor cloud-native optimizations during migration.
- Refactor/Rearchitect: Rebuild applications using cloud-native features for maximum benefit.
- Repurchase: Switch to a SaaS solution.
- Relocate: Move virtual machines to a new environment without new hardware.
- Retain: Keep applications on-premises if there’s no business case to move them.
- Retire: Decommission applications that are no longer needed.
- Setting Timelines and Milestones: Establish realistic timelines and milestones to track progress and manage expectations. Use pilot projects to test your approach on lower-risk applications first.
- Budgeting and Resource Allocation: Understand the financial shift from capital expenditure (CapEx) to operational expenditure (OpEx). A cost-benefit analysis is crucial for effective resource allocation and cost control.
- Leveraging a Cloud Adoption Framework: Use a structured cloud adoption framework to guide your efforts across business, governance, security, and operations. For more on strategic planning, see our Business Agility Consulting Guide 2025.

Developing Your Cloud Adoption Strategy: A Step-by-Step Framework
The journey continues post-migration with continuous management and optimization. A successful cloud adoption strategy requires a robust operational framework to maximize value.
- Cloud Operations Strategy: Define how you’ll manage cloud environments post-migration, focusing on scalability, reliability, monitoring, and business continuity to maximize performance and efficiency.
- Managing Cloud Environments: Implement automation for routine tasks like scaling and patching. Enforce clear access control policies to secure systems and data. For expert guidance, consider IT Consulting Services.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously track key metrics like resource utilization and application performance. This data-driven approach helps identify bottlenecks and ensure service levels meet business goals.
- Cost Optimization (FinOps): Implement cloud financial management to ensure cost transparency and predictability. Regular audits and utilization monitoring are vital to prevent uncontrolled spending.
- Security Management: Cloud security is a shared responsibility. You are responsible for securing data, applications, and access. Your strategy must include encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular audits, and incident response plans.
- Measuring Success with KPIs: Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like cost savings, system uptime, and time-to-market to measure success. This allows you to monitor performance against strategic goals.
- Continuous Evaluation: The cloud landscape is always changing. Your strategy must be an iterative process, regularly revisited to adapt to new technologies and business needs.
Navigating Common Cloud Adoption Challenges
Even with a solid plan, challenges can arise. A robust cloud adoption strategy anticipates and addresses them.
- Security and Compliance Risks: The cloud can introduce new vulnerabilities. Address this with pre-adoption assessments, strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and adherence to all relevant compliance standards.
- Cost Management and Budget Overruns: Uncontrolled cloud costs can escalate quickly. Implement continuous cost monitoring and FinOps practices to maintain financial efficiency.
- Vendor Lock-in: Relying on a single provider limits flexibility. Adopt a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy to leverage different providers and avoid over-reliance.
- Overcoming the IT Skills Gap: A need for more qualified staff was the biggest challenge to faster cloud adoption for organizations in 2023. Address this by investing in training, upskilling existing teams, and considering external partnerships.
- Change Management: Cloud adoption is a cultural shift. Overcome resistance with clear communication, training, and early stakeholder engagement to ensure a smooth transition.
- Data Governance: Managing data in the cloud is complex. Establish a strong data governance framework to control data residency, access, and quality while maintaining compliance.
Future-Proofing Your Cloud Adoption Strategy with Emerging Trends
The cloud landscape is dynamic. To maintain a competitive edge, your cloud adoption strategy must be agile and incorporate emerging trends.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and ML are becoming integral to cloud operations, improving everything from customer service to fraud detection. Our AI Adoption Strategies Complete Guide explores this in detail.
- Rise of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: These models are now standard practice, allowing organizations to optimize costs, ensure resilience, and avoid vendor lock-in by using the best services from different providers.
- Edge Computing: This brings computation closer to data sources, reducing latency for real-time applications in manufacturing, retail, and autonomous systems.
- Serverless Architecture: Run code without managing servers. This model reduces operational overhead, scales automatically, and lowers costs by only charging for compute time used.
- Sustainability in the Cloud: Green IT is a growing focus. Leverage cloud providers committed to sustainable infrastructure to reduce your organization’s carbon footprint.
Chris Robino’s expertise helps organizations steer these shifts, ensuring technology drives business innovation. To stay ahead, explore more technology trends for business and adapt your cloud adoption strategy accordingly.
